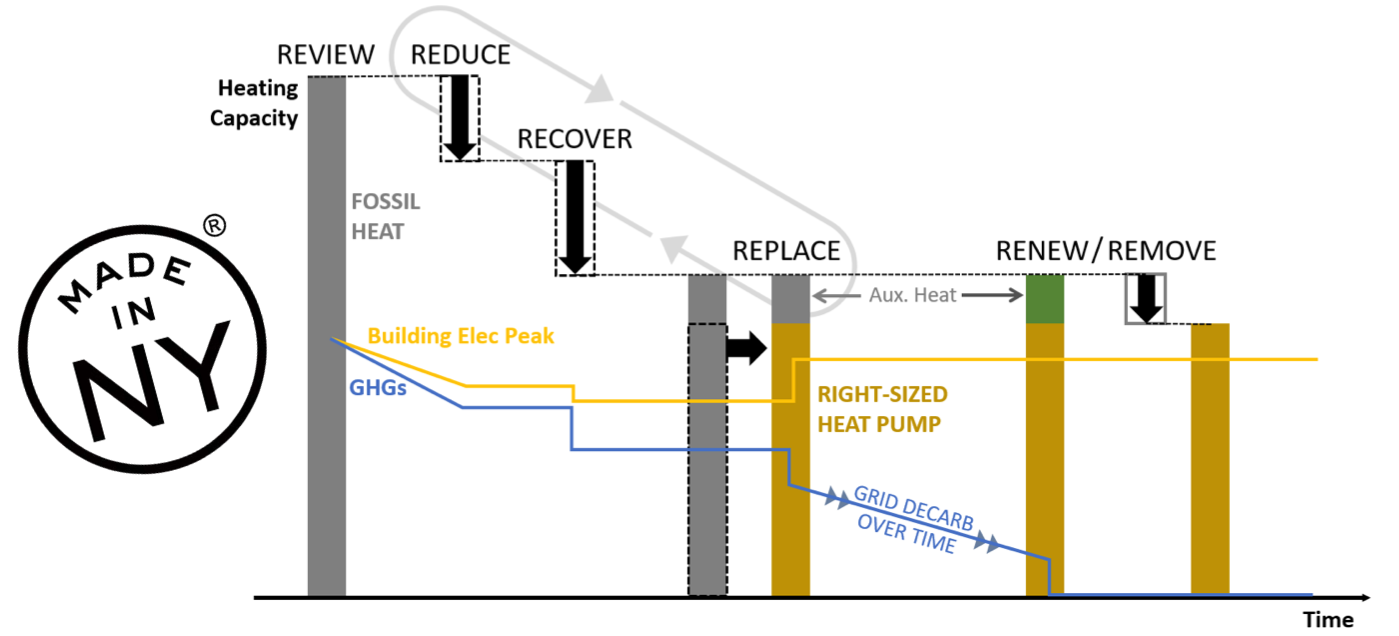
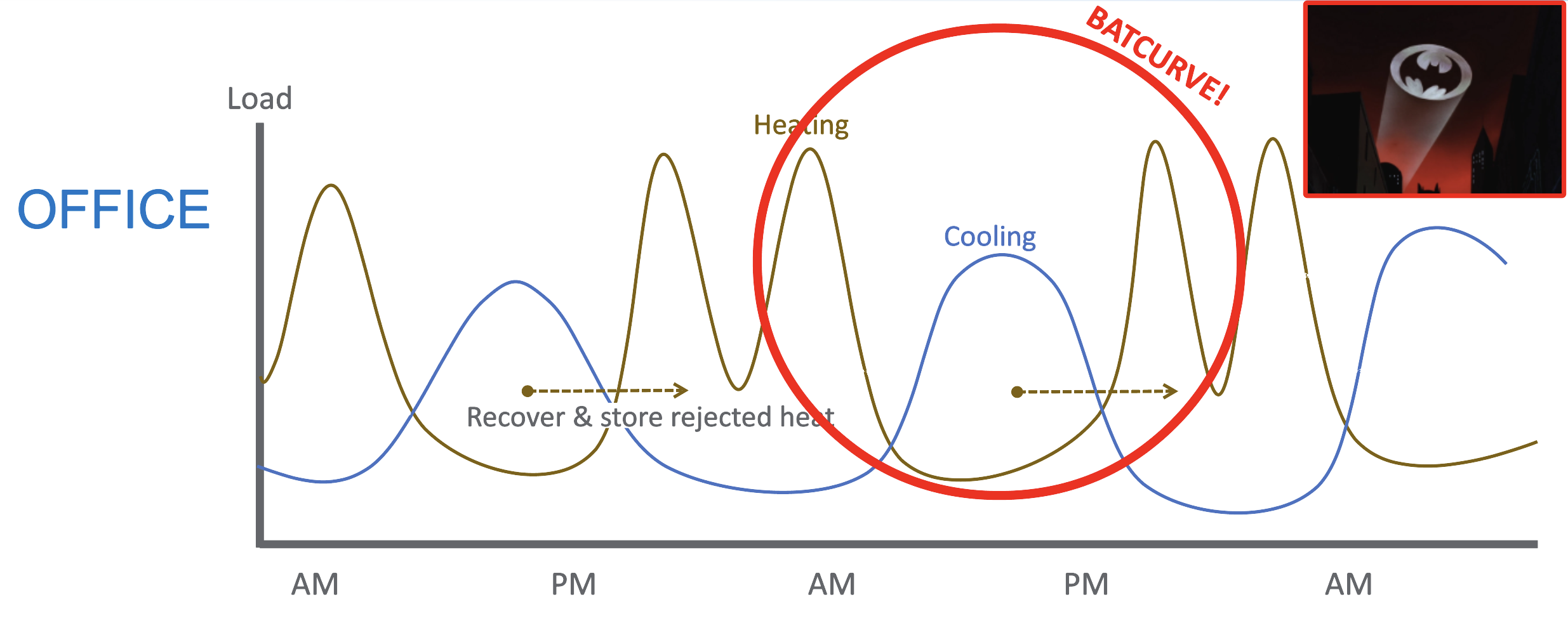
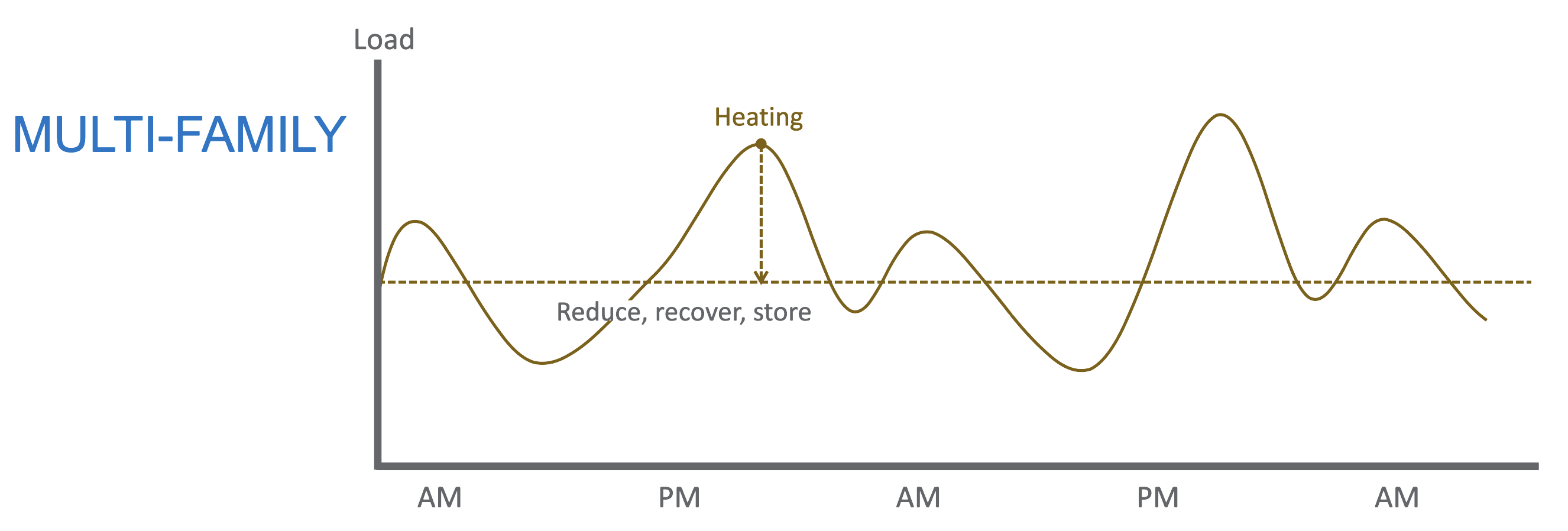
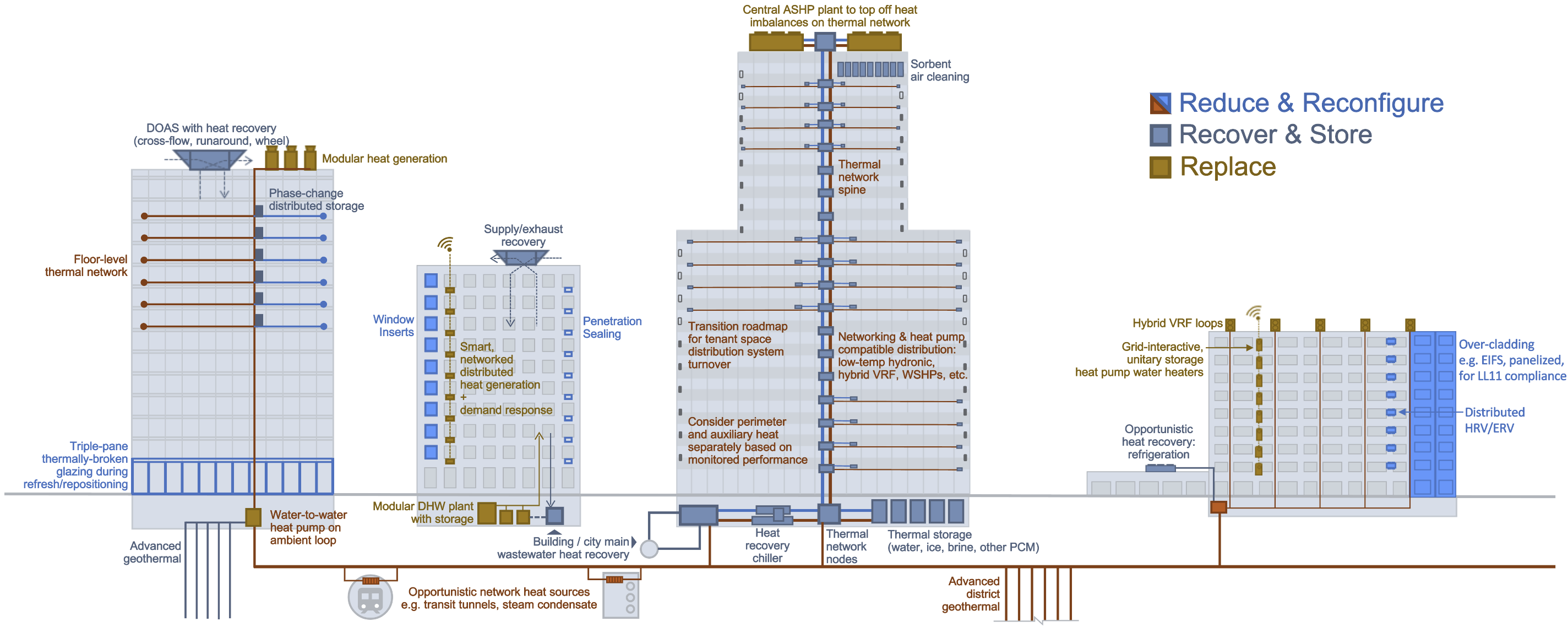
New engineering design means and methods are needed to enable and speed adoption of low carbon retrofit technologies. Efficient heating and cooling energy systems are widely available but underused due to lack of knowledge and thermal system interaction. Decarbonization requires adapting distribution designed for legacy thermal supply to electric and renewable thermal energy systems. The solution is Resource Efficient Electrification (REE). This novel approach emerges from the Empire Building Challenge after one year of collaboration between real estate partners, industry-leading engineering consultants and the NYSERDA team. REE is a design strategy which can help alleviate space constraints issues, provide peak thermal capacity, optimize operational efficiencies, utilize waste heat, and reduce the need for oversized electrified thermal energy systems creating retrofit cost compression. It is a framework of building decarbonization tailored to cold climate tall buildings but that can be applied across New York’s, wide array of building types, vintages and systems. This heuristic incorporates strategic capital planning, an integrated design process, and an incremental, network-oriented approach to deliver building heating, cooling, and ventilation which: - requires limited or no combustion,
- enables carbon neutrality,
- is highly efficient at low design temperatures and during extreme weather,
- is highly resilient, demand conscious, and energy grid-interactive,
- reduces thermal waste by capturing as many on-site or nearby thermal flows as possible, and
- incorporates realistic and flexible implementation strategies by optimizing and scheduling low carbon retrofits phase-in.
|